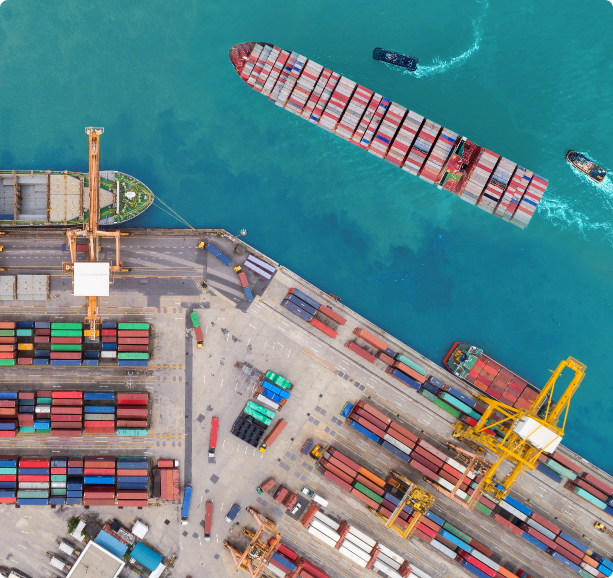
Asian shipowners with vessels sailing to and from Europe are likely to face estimated emissions liabilities of over €1 billion once the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is fully implemented, with companies registered in China and Singapore bearing the highest burden, according to OceanScore.
The Hamburg-based maritime technology firm has calculated that Asia-based Document of Compliance (DoC) holders will ultimately have to surrender a total of between 15-16 million EU Allowances (EUAs), or carbon credits, for voyages to and from the EU that are liable for 50% of emissions, while port calls and transits within the EU are liable for 100% of their emissions.
OceanScore estimates EU ETS costs for Asian owners of around €500 million this year when they will be liable for 40% of their emissions, rising to 70% in 2025 and 100% in 2026 under the three-year phase-in of the regulation.
The EU ETS, implemented from 1 January 2024, will affect around 4000 Asian-flagged vessels, or about one-third of the total 12,500 cargo and passenger ships above 5000gt that are currently subject to the EU ETS, according to the company.
These are owned or operated by 400 DoC holders, including major players like China’s COSCO, Hong Kong-based Anglo Eastern Ship Management and South Korean HMM, with around half of affected vessels operated by non-EU DoC holders.
EU ETS costs a moving target
The total €1 billion cost estimate for Asian shipping, based on the expected volume of EUAs set to be surrendered by regional DoC holders from 2026, is contingent on the volatile carbon price that is currently at a relatively low level of around €55 per tonne of CO2 after fluctuating between €80-100 last year.
The carbon price is dictated by supply and demand for EUAs, with the volume of allowances available for trading set to be gradually reduced over time under the cap-and-trade system to incentivise investments in measures to cut ship emissions.
OceanScore’s co-Managing Director Albrecht Grell says a total of nearly 80 million EUAs will have to be surrendered by the shipping industry once the EU ETS is fully phased in, of which 40% will come from non-EU companies, also including the UK, Norway and Turkey.
OceanScore forecasts that, at full phase-in, around 5.5 million EUAs will have to be surrendered by Chinese and Hong Kong-based entities and 5.4 million by Singaporean players, with the remainder coming from Japan (1.6 million), South Korea (1.2 million) and India (1.1 million). When other Asian countries such as Thailand and Malaysia are included, the total number of EUAs required rises to 20 million.
In a breakdown of costs exposure for individual companies, OceanScore has calculated that a company with 15 vessels would be required to surrender just over 300,000 EUAs, which would equate to a cost of €16.5 million based on the current carbon price.
Catching up with regulatory changes
Voyages into and out of Europe account for around 59% of emissions covered by the EU ETS, versus 41% for voyages and port calls within Europe, but will still have a lower cost burden than domestic European traffic due to the 50% liability factor.
Long-haul voyages into the EU can be broken up by stopping at transshipment ports to reduce emissions exposure, but Grell says “we don’t see many people seriously discussing this” due to the negative impact on fuel costs, waiting times, additional sailing distance and other inefficiencies.
Asian players represent around 25% of the overall 1700 DoC holders that now must relate to the regulation, which is in particular focusing the minds of European owners with an EU-centric deployment pattern for their vessels.
“Consequently, we see that European owners generally have started to prepare earlier for compliance with the EU ETS as it is closer to home and is therefore perceived as having a more tangible financial impact on their operations,” Grell says.
“It is also typically easier for companies domiciled in the EU to set up Union Registry accounts required for handling EUAs, as well as gain access to trading platforms, which is more difficult for those based in non-EU countries given sometimes quite complex Know Your Customer (KYC) processes”
As well as these administrative obstacles, he claims non-EU players have been put at a disadvantage by having to play catch up with the late finalization of Implementation Acts by the EU to avoid being wrongfooted when having to collect and later surrender EUAs. Among these measures, the shipowner has been assigned responsibility for reporting emissions and surrendering EUAs, though it can be transferred to the technical manager if an agreement along these lines is in place.
‘Stepwise approach’
OceanScore is now assisting both EU and non-EU-based shipping companies in setting up administrative systems to navigate the complexity of the EU ETS, predicated on its web-based ETS Manager that provides an end-to-end solution to support management and trading of EUAs.
This efficiently runs the process of allocating, requesting and collecting EUA from charterers based on different charter parties, with full transparency on all related data flows. Furthermore, ETS Manager monitors Union Registry accounts for EUAs and minimizes risks with open EUA positions by identifying missing allowances that need to be collected.
“It is vitally important that non-EU actors engaged in trading vessels to and from the EU also become fully up to speed with the regulation and put systems in place to manage and mitigate their EUA liabilities,” Grell says.
“This requires a stepwise approach by opening Union Registry accounts, amending the Shipman management agreement, incorporating relevant EU ETS clauses like those from Bimco in the charter party and securing access to EUAs. And, not least, finding a trustworthy and reliable partner with the necessary expertise to digitalize the various processes efficiently, as doing this in-house can be risky, laborious and expensive.”