Shipping companies are facing significant financial exposure from the introduction of the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) next year, which will increase balance sheet risk, further fuelled by carbon price volatility and the threat of fines for non-compliance. The big question is: Who will foot the bill?
And that bill will be substantial. In 2022, the maritime industry generated CO2 emissions of 126m tonnes from voyages to, from, between and within European ports that would have resulted in the need to surrender 82.7m EU Allowances (EUAs), or carbon credits, under the EU ETS, equating to a total cost of €6.5bn based on the current price of €78 per EUA that corresponds to a tonne of CO2.
This figure is based on full implementation of the EU ETS in 2026 after a three-year phase-in period, with 68% of emissions last year generated on voyages into or out of EU ports, which will incur costs for 50% of emissions, and the remaining 32% between or within EU ports that are liable for 100% of emissions.
Counting the cost for ship segments
Container shipping, not surprisingly, will account for the largest part of the industry’s total emission costs at around 28%, followed by the Ro-Pax segment with 14%, while bulk carriers and tankers are set to carry around 11% apiece, according to OceanScore analytics based on EU MRV data.
However, on a per-vessel basis, it is cruise and Ro-Pax ships that will have to bear the largest burden with annual EUA costs for the respective vessel type estimated at €2.8m and €2.5m. By contrast, the average bulker, while being the largest segment with 30% of all vessels in the EU ETS regime, will only see EUA costs of €208,000 annually.
The sheer size and hotel load of the cruise sector and the deployment patterns and speeds of Ro-Paxes have a significant impact on their carbon footprint, with these vessels accounting for nine out of 10 of the top contributors to emissions under the EU ETS, with over 100,000 tonnes of CO2 per vessel annually. The highest emitter in European waters is a cruise vessel with 134,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions per year.
At a country level, given fleet structure and typical voyage patterns, the shipping industry in Turkey, for example, would be required to buy and surrender EUAs for a total of €200m, which translates into nearly €400,000 per vessel.
EU ETS Compliance for Shipping Companies: Mitigating EUA Liabilities
Each shipping company, as the Document of Compliance holder or vessel owner (EU regulation on the ETS responsibility is still in the process of being finalised), must determine the volume of EUAs to be purchased and surrendered to compensate for its emissions in any given year based on MRV data.
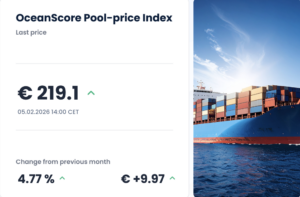
The overall cost will be largely dictated by the EUA price, which historically has proven highly volatile. While it has dropped to €78 in recent weeks, the price is set to be driven upwards over time due to high demand and an annual 4.3% reduction in the number of available allowances under the cap-and-trade system, incentivising investments in efficient operations, carbon reduction technologies and alternative fuels.
Furthermore, there is the risk of penalties for failing to surrender the required number of EUAs, with a fine of €100 per allowance in addition to the cost of acquiring additional EUAs to make up the shortfall. Failure to comply on any vessel for more than two years running could risk an EU trading ban for the entire fleet.
A key factor for shipping companies in tackling EUA liabilities and risks is an efficient EU ETS management system with accurate tracking of emissions data, both to determine the correct volume of allowances required – also covering for offhire and periods of unemployment, as well as considering all the exemptions, discounts and regulatory details – and ensure correct allocation of EUAs to charterers (based on the EU’s ‘polluter pays’ principle) and owners with proper monitoring of all EUA provisions, open positions etc.
Risk of disputes
A solution to efficiently manage these processes and assure transparency and control is a vital prerequisite to mitigating the inherent risks of the EU ETS regulation to a shipping company. Any such system will need to be based on solid data to reduce the risk of disputes between charterers, owners and managers.
A whole range of solution providers have sprung up recently, from MRV verifiers to vessel performance management solutions providers to consultants. Most of these systems provide data at a level of granularity and data quality that can serve as input into an integrated ETS management process, with solution-specific issues remaining to be compensated for.
Shipping companies will need to set up so-called Union Registry accounts to receive, buy and manage EUAs, and to later surrender them to the respective authorities. Setting up these accounts as well as getting access to EUA trading solutions via banks or brokers will be necessary. This requires having EUA accounts in Europe and monitoring these, putting in place an EUA trading solution and managing potential disputes in the process.
Clearly, reducing emissions at the operational level is another means of cutting EUA costs exposure but the industry has so far been able to make lacklustre progress in this area, with a reduction of only 0.14% for ships in EU waters since 2021, driven by fewer vessels sailing fewer nautical miles.
Emissions per nautical mile actually increased by 3.09% last year, driven by changing operational patterns and higher speeds in some segments – outweighing the many efficiency-oriented measures put in place in recent years. Still, emissions of 411 tonnes of CO2 per 1000 nautical miles are way below any alternative transport option, a testament to shipping’s efficiency.
Shift in the right direction
In the bigger picture, the EU ETS appears well-designed and is leading shipping in the right direction. The current price of EUAs adds more than 50% to the cost of bunkers.
As a result, the competitive advantage with newer, more efficient tonnage versus less efficient tonnage will increase, impacting the chartering market, the second-hand market and deployment patterns. The upcoming regulation will enhance business cases for energy-saving projects, improve operations and, in the long run, for cleaner fuels as well.
Our analysis indicates that shipping companies are correctly focusing on increased efficiency, making fears of substantial evasive behaviours seem unjustified, so far at least.
The EU ETS regime will further accelerate the trend towards digitalisation and data transparency. In the end, the winners in the EU ETS regime will not be those able to buy EUAs at a 10cts discount but those that are able to efficiently manage their related processes and risk exposure.
For more information contact:
Albrecht Grell, co-Managing Director, OceanScore.
Email: albrecht.grell@oceanscore.com